This section briefly describes the VPN network embedded on ZEVENET Load Balancer. The virtual private network allows flexible and scalable privacy and data protection through high-end encryption methods like AES-256, blowfish-256, and camellia-256, and authentication methods like MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-256. Market standard protocols like L2TP/IPsec, IKEv1, and IKEv2 are supported.
The appliance allows users to create a desired VPN profile depending on the nature and purpose of use from client. The three supported VPN profiles are;
ZSS. This type is a ZEVENET Site to Site VPN. This mode could be used from clients to load balancer or load balancer to real servers. ZEVENET will be the default gateway for each local and remote subnets. IPSEC implementation.
ZTN. This type is a ZEVENET Tunnel VPN. This mode creates a GRE tunnel over IPSEC implementation, also could be used from clients to load balancer or load balancer to real servers. ZEVENET will be the default gateway for each local and remote subnets.
ZRS. This type is a ZEVENET Remote Site VPN. ZEVENET acts as a VPN server, so the clients could connect to such VPN and they will assign a dynamic IP address to be routed later on via the routing system. IPSEC implementation in server mode for clients in mode road warrior.
VPN Network List
The figure below shows a table of created VPN networks and the associated properties.
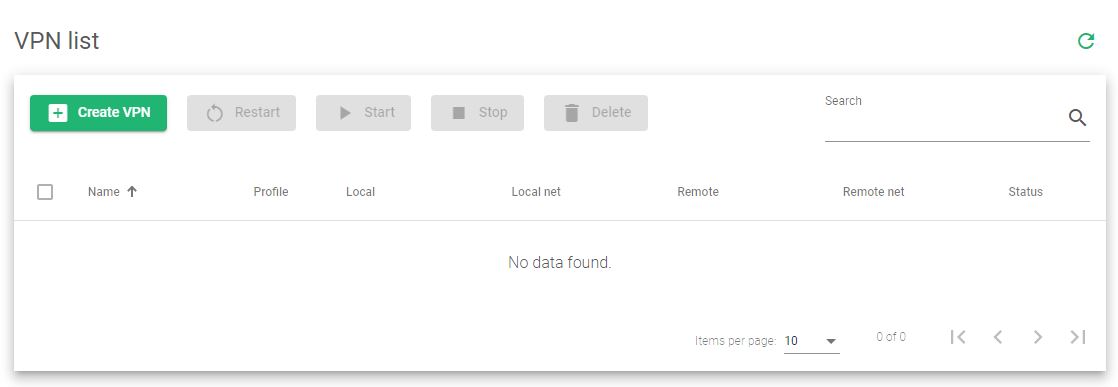
Here is a brief description of each table property.
Name. A label that easily identifies a VPN profile on the appliance.
Profile. The type of VPN to use, whether it is a site-to-site or remote access VPN.
Local. The IP address of the local server if it is configured. Supports both IPV4 and IPV6.
Local net. The subnet mask of the local server if it is configured. You must configure this netmask when you set up the IP of the local server.
Remote. The network layer IP address of the remote server if it is configured. Supports both IPV4 and IPV6.
Remote net. The subnet mask of the remote server if configured. You must configure this netmask when you set up the IP of the remote server.
Status. Shows the health indicators of a VPN created and listed on the table. Here is a brief description of what each color means.
- Green. If the VPN is UP.
- Red. If the VPN is DOWN.
Actions. These are the available actions for managing a selected VPN profile.
- Create VPN. Shows a form and the fields used to create a VPN profile.
- Restart. Reboots a VPN profile in case it slows down or becomes unresponsive.
- Start. Activates a selected VPN profile and configures it to allow packets to flow through the associated IP address.
- Stop. Deactivates a selected active profile and prevents it from accepting packets.
- Delete. Removes a VPN profile from the table list and its associated configurations.