This section explains how to create a VLAN interface and the different options available.
Create VLAN
Find the detailed descriptions for creating a VLAN below.
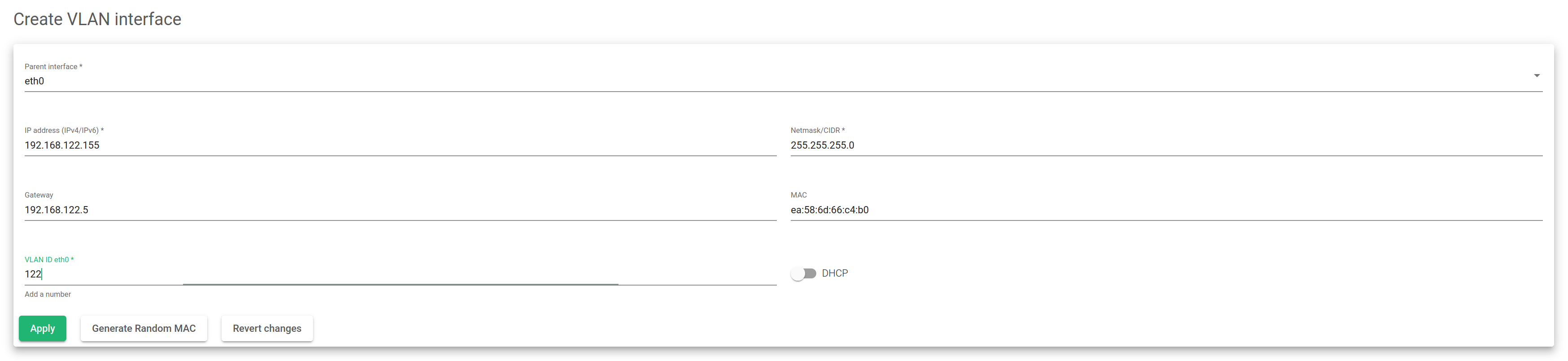
Parent Interface. Select the VLAN parent interface. Select either a NIC or a Bonding interface.
IP Address. The network-layer IP address for the new VLAN. It supports IPv4 and IPv6. This field is mandatory and the Netmask field must also be set if DHCP is disabled.
Netmask/CIDR. The Netmask field supports Network mask format or CIDR (0 to 32 bits) when using IPv4 or only CIDR format (0 to 128 bits) when using IPv6. This field is mandatory and the Address field must be also set if DHCP is disabled.
Gateway. Sets a default gateway for this VLAN interface. This field is not mandatory.
MAC. For the link-layer MAC address for the new VLAN. You can generate a random valid MAC address by clicking on the generate random MAC button or a custom MAC address. In case a custom MAC address is set, it should be used with caution to avoid MAC address duplication.
VLAN ID. The name of the new VLAN interface as will be stored in the system. It starts with the name of the Parent Interface followed by the VLAN tag separated by a dot. The Parent Interface name plus ‘.’ (dot) plus the VLAN name set must be lower than 16 as defined by the system.
DHCP. Enables the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the VLAN interface. This option will require a DHCP server running on the VLAN tag configured, and it must be reachable.
IPv4 and IPv6 stacks are supported, taking into account that the Netmask and Gateway must be configured in the same stack as the IP.
Once all the required changes are done, press the Apply button to create the new VLAN interface. If you’re unsatisfied with the current changes, you may revert to the previous configuration by clicking the Revert changes button.