Floating IPs (FIPs) and How they can save your business.
A floating IP is a type of virtual IP address not assigned to load balance service, but assigned to routing outgoing traffic from a given output interface in the load balancer to the Backends. In simple terms, it’s an IP address that is shared and “ floats” between both nodes of the cluster for routing purpose.
In other terms floating IPs use IP addresses from Virtual Interfaces to masquerade the outbound traffic despite they’re going over a NIC, VLAN or Bonding interface in both nodes of the cluster. So when the cluster changes its master role, services (I.e. Farms) created over a Floating IP of the cluster will be switched from one node to another transparently without affecting to the clients, backends connections or data streams.
Let’s say you have an application load balanced on two servers, A and B. Server A will be receiving traffic from the output IP of the load balancer, (floated IP). The MASTER load balancer should experience downtime or any technical difficulty, the current traffic is created between the floating IP in this load balancer and the backend IP, instantly the Load Balancer cluster service will do its job and will move the service to the other node of the cluster,
and will continue moving traffic with the same floating IP, so the connection tracking system in the load balancer will be able of continuing moving traffic and the backend will not notice any downtime. Now, Load balancer node two will be active while the previous MASTER undergoes maintenance.
In a business community where downtime may cost fortunes, it requires that you have your servers up all the time to process client requests.
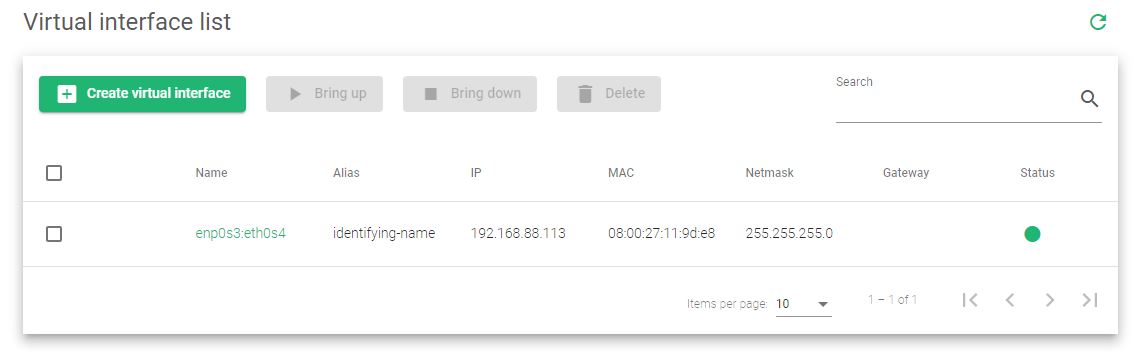
Floating IPs Table
The image below shows Zevenet EE v.6.2 table with a floating IP address that has been configured to the system.
These are the descriptions of the fields from the image above.
Interface. Name of the parent interface. This could be VLAN, bonding, or a NIC interface.
Interface Ip. The IP address of the parent interface.
Interface alias. A memorable name that easily identifies the parent interface.
Interface Virtual. The name of the virtual interface from which you’ll select the floating IP.
Floating IP. Shows only a configured IP address inherited from the virtual interfaces.
Actions. Use the following actions to set up a floating IP.
- Configure. Assign a floating IP address to the parent interface. Only one floating Ip can be assigned.
- Unset. Clears the configuration and removes the virtual IP address.