Zevenet Load Balancer is designed to be integrated into as many subnets as needed, so with this premise, the system has been designed with a routing system based in rules an tables, the rule is the condition that the packet has to match in, and the table is where the packet is sent if the rule matches.
Each table knows the other subnets just to ensure if the packet reaches a VIP in a table the packet is forwarded to the backend through the same table, in case that the backend is not reachable directly through one already configured subnet in the load balancer then the packet will be forwarded to the Gateway of the used VIP’s routing table.
Once the packet is replied of the backend, the rule table has to ensure that it is will be managed by the same table than was sent previously to the backend in order to avoid asymmetric routes.
It is important that the same subnet is not configured in the load balancer into more than one interface, because in that case, the rule table will not be able to decide which routing table is responsible of the packet itself.
But the behaviour described previously can be modified if needed, and the users can add their own rules and route tables modifying the Routing module to adapt it to the individual needs.
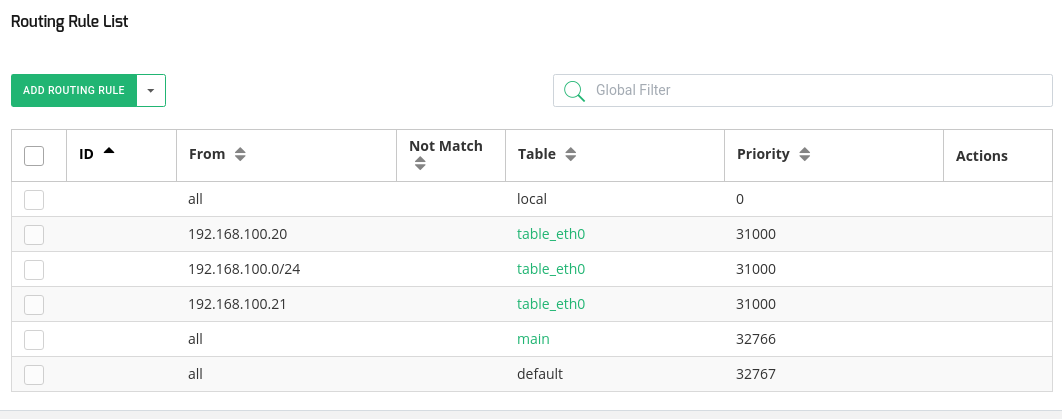
The Rules table is described below:
This table shows the rules already configured in the system, the fields are described below:
ID: A unique internal identifier assigned to the rule, this value can’t be configured or modified.
From: This field accepts IP or CIDR (IP/bitmask), the source which the packet has to come from.
Not match: this field is used to deny the rule.
Table: The table where the packet will be sent and where the routes will be applied.
Priority: The priority of the rule, the priority can be altered but by default, the system assigns a value, less value more priority.
Actions: The actions for the default rules are hidden, this field allows to modify or delete the given rule.
Bulk actions:
Delete: The rule will be deleted of the rule table
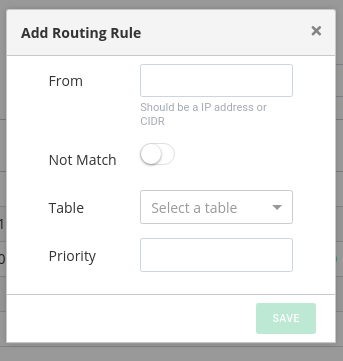
Add routing rule
From: Indicates the IP or CIDR (IP/mask) where the packet come from.
Not match: A check which is used to negate the condition, by default disabled.
Table: Which routing table to send the packet to when From matches.
Priority: Indicates a priority value in order to be managed by the rule table.