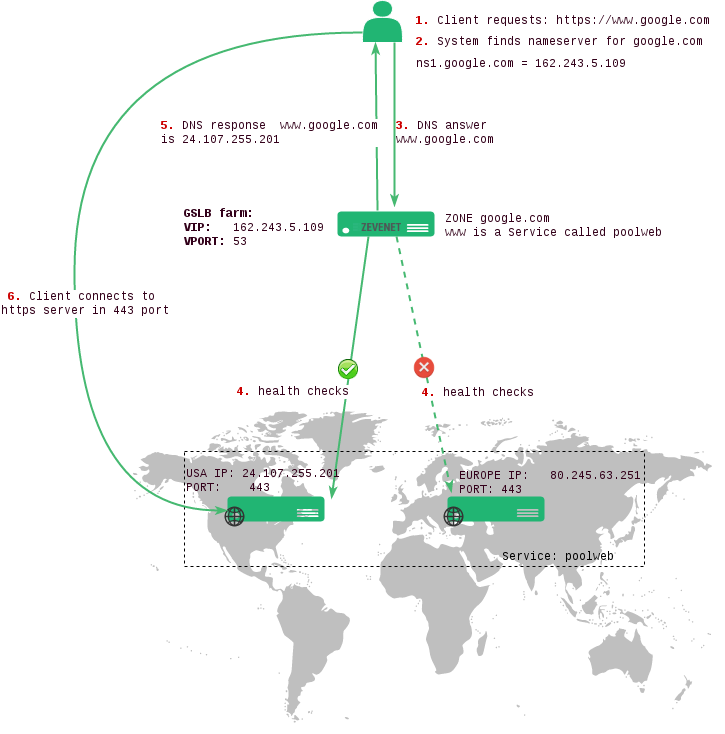
The Global Service Load Balancing, commonly called GSLB, allows creating a load balancing service based on the DNS service hierarchical architecture. This kind of farm provides an authoritative-only DNS with load balancing algorithms and service state detection at DNS application layer.
Under this section, you’ll be able to manage the GSLB (Global Service Load Balancing) farms module. This profile is able to control all kinds of services and applications using the DNS layer to deliver the most suitable server to the client, creating a distributed and geolocated service across different data centers.
In the scheme below is shown the common use case for load balancing across different data centers using GSLB infrastructure an HTTPS webpage (ex. google.com).
Actions Sub-menu
Through the scroll-down menu the following actions are available for selected farms:
- Create Farm. Create a new farm managed by the GSLB module.
- Restart. Stop and start again a farm service in the GSLB module.
- Stop. This action stops the selected farm’s services.
- Start. This action starts the selected farm’s services.
- Delete. This action stops the services and deletes the farm’s configuration and connection stats.
The actions will be executed in batches in all the selected farms (multiple selections available).
Content Table
Lists the properties of every farm.
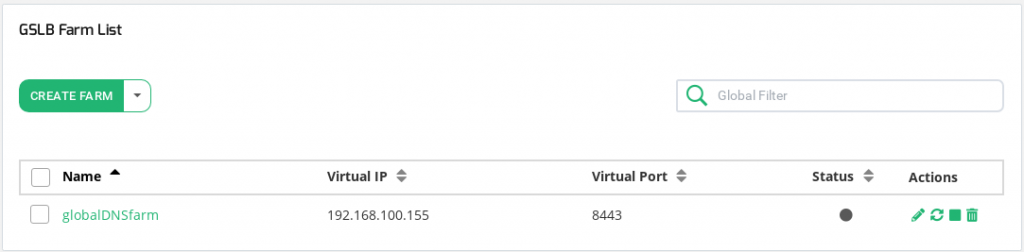
The fields shown per farm are described below.
Name. A descriptive name for the farm, this value will be unique in all the virtual services created.
Virtual IP. The IP address that is managing the incoming traffic.
Virtual Port. The port that is managing the traffic. As this service behaves like a DNS service, usually it would be the port 53 UDP.
Status. The status of the given farm, the available values are
- Green: Means UP. The farm is running and all backends are UP.
- Red: Means DOWN. The farm is stopped.
- Yellow: Means RESTART NEEDED. There are recent changes that need a farm restart to be applied.
- Black: Means CRITICAL. The farm is UP but there is no backend available or they are all in maintenance mode
- Blue: Means PROBLEM. The farm is running but at least one backend is down.
ACTIONS. The available actions/icons for every farm in the table are the following:
- Edit. Change the basic and advanced options for this virtual service or farm, create new services and apply changes to the backends.
- Restart. The Farm will be stopped and started automatically.
- Stop. This action is only available if the farm is running and all the traffic managed by this farm will be dropped once the button is pressed. The PORT will be released so, it will be able to be used by another profile.
- Start. This action is only available if the farm is stopped, the service will bind to the configured IP and PORT and hence the traffic through them will be handled by the farm.
- Delete. The Farm will be stopped and all the configuration files deleted. The IP and PORT will be released so it could be used by another farm.
Check out our video about GSLB.