Virtual Interfaces permits to assign more than one IP address per each NIC, Bonding or VLAN interface configured in the system. See below how to configure and manage Virtual Interfaces.
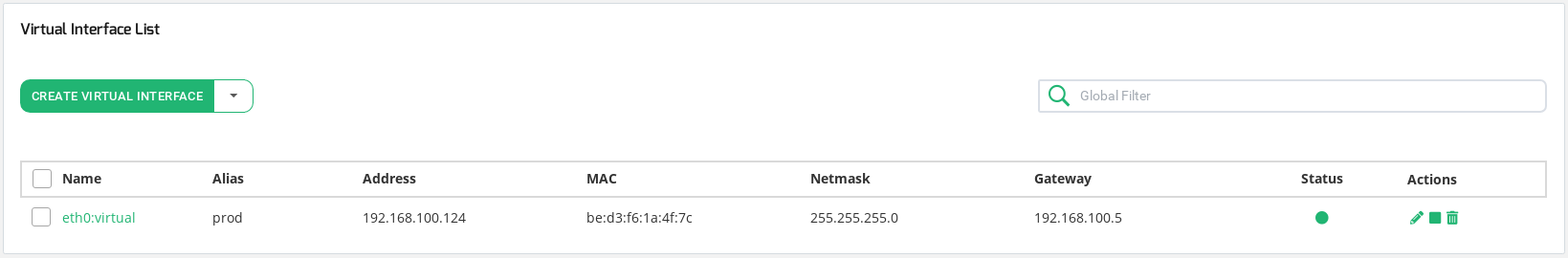
Virtual Interfaces Table
This table lists all the Virtual Interfaces configured in the system.
NAME. Name of the virtual interface.
ALIAS. Interface alias, it identifies the interface with an alias that can be easily accessed when configuring a farm or any other service.
ADDRESS. Network-layer IP address assigned. Supports IPv4 and IPv6.
MAC. Link-layer MAC address of the interface. It is inherited from the parent NIC interface.
NETMASK. The subnet mask of the parent NIC. It can only be configured if the IP address is configured too.
GATEWAY. Default gateway used by the virtual interface if configured. Inherited from the parent interface.
STATUS. The status of a given virtual interface, the available values are Green if the virtual interface is up and Red if the virtual interface is down.
ACTIONS. The available actions for every virtual interface in the table are the following:
- Edit. Change the virtual interface configuration like its IP address or its alias.
- Bring up. Set the interface up to accept traffic.
- Bring down. Set the interface down and stop accepting traffic.
- Delete. Clear the configuration and remove the virtual interface.
Through the Actions menu button the following actions are available for the selected interfaces:
- Create a Virtual Interface. This option redirects to the Virtual Interface creation form.
- The actions mentioned above. The same actions as mentioned above: Bring up, Bring down and Delete