VLAN interfaces (also known as VLAN tagging) permits to isolate logical networks architectures at OSI layer 2 over the same physical NIC interface, each one with it’s own independent routing table. See below how to configure and manage VLANs interfaces.
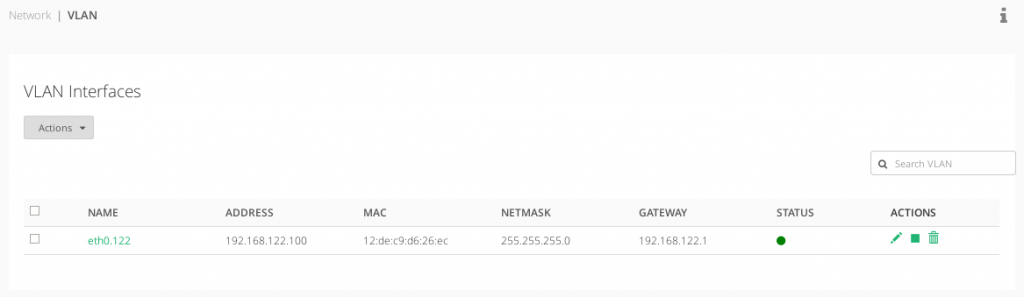
VLAN Interfaces Table
This table lists all the VLAN interfaces configured in the system.
NAME. Name of the VLAN interface.
ADDRESS. IP address assigned, if any.
MAC. Hardware address of this interface. It’ll be inherited from the parent NIC interface.
NETMASK. Subnet mask assigned, if the interface is configured.
GATEWAY. Default gateway used by the VLAN interface.
STATUS. The status of a given VLAN interface, the available values are Green if the virtual interface is up and Red if the virtual interface is down.
ACTIONS. The available actions for every interface in the table are the following:
- Create VLAN. A new VLAN interface needs to be created.
- Delete. Unset the configuration and remove the VLAN interface.
- Edit. Change the VLAN configuration like IP address, netmask and gateway.
- Bring up. Set the interface up and configured to accept traffic.
- Bring down. Set the interface down and stop accepting traffic.
- Cluster. No actions are allowed as this interface is used in the cluster service for synchronization and heartbeat processes. In order to modify this interface is required to disable the cluster service.
The actions will be executed in batches in all the selected VLANs through the multiple selection option.